The work of a cybersecurity professional is more than the stereotypical picture most people have of a computer science major or a hacker, skills are needed from a diverse range of backgrounds. Cybersecurity also plays a vital role in the lives of all and the cybersecurity workforce makes a difference in our world. Building a national cybersecurity workforce enhances national security and promotes economic prosperity. You may be surprised but modern-day cybersecurity actually first began to come about in the 1970s.

The History of Cybersecurity
Believe it or not, the idea of a computer virus preceded computer networks. Mathematician John von Neumann predicted the idea in the late 1940s, but it wasn’t until 30 years later before someone actually created one. In 1971, Bob Thomas made history by creating a program, known as Creeper, that is widely accepted as the first-ever computer worm. A worm is a type of computer virus that replicates itself and spreads to other systems. Unlike today’s malicious viruses, all Creeper did was display a message on any infecting screen stating, “I’m the creeper: catch me if you can.”
Over the years that followed, computers started to become more and more connected, computer viruses became more advanced, and information security systems could not keep up with the constant barrage of innovative hacking approaches.
In 1988, the world saw the birth of the Morris Worm – one of the major turning points in the history of information security. Named after its inventor Robert Morris, the worm was designed to propagate across networks, infiltrate terminals using a known bug, and then copy itself. Its aim was to identify lacking areas in a network intrusion prevention system. However, its ability to self-replicate would be its downfall, as the worm replicated so aggressively that it rendered targeted computers inoperable and slowed the internet down to a crawling pace. It also spread quickly throughout the network and caused untold damage. In fact, the damage it caused was so severe that Robert Morris became the first person to become successfully charged under the Computer Fraud and Misuse Act.
By the middle of the 90s, network security threats had increased exponentially, and as such, firewalls and antivirus programs had to be produced on a mass basis to protect the public. It was a NASA researcher who created the very first firewall program design, following a computer virus attack at their California base. The research and their team created a virtual ‘firewall’ which they modeled on the physical structures that prevent the spread of actual fires within buildings or structures.
In the early 2000s, governments began to clamp down on the criminality of hacking, giving much more serious sentences to those culpable – including extensive jail time and large fines. Information security continued to advance as the internet grew as well but, unfortunately, so did viruses. Hackers quickly became able to create viruses that could not only target specific organizations but whole cities, states, and even continents as well. In 2003 Anonymous became the first universally known hacker group. The group has no leader and represents many online and offline community users. The group gained national attention when they hacked the Church of Scientology’s website.
Due to the consistent rise of technology, hacking has become even more complicated over the past few years, and a number of major data breaches now largely define the era. These include:
- Yahoo, 2013 – 2014. Hackers broke into Yahoo, jeopardising the accounts and personal information of their three billion users. They were fined $35 million for failing to disclose news of the breach in a timely manner, and Yahoo’s sale price decreased by $350 million as a result.
- WannaCry, 2017. More widely known as the first ‘ransom-worm’, WannaCry targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system and demanded ransom payments in the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. In only one day, the worm infected over 230,000 computers across 150 countries.
In recent years, massive breaches have hit name brands like Target, Anthem, Home Depot, Equifax, Yahoo, Marriott, and more – compromising data for the companies and billions of consumers. In reaction, stringent regulations to protect citizen privacy like the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the new California Consumer Privacy Act are raising the bar for compliance. To keep up, the cybersecurity industry is constantly innovating and using advanced machine learning and AI-driven approaches, for example, to analyze network behavior and prevent adversaries from winning.
Careers in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is one of the largest growing fields. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job market for information security analysts will grow by 32 percent by 2028 — making it one of the fastest growing job sectors — while Cybersecurity Ventures has found that there will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs in 2021. This means that cybersecurity professionals are among the most in-demand around the world and will be for years to come.
Jobs in this field consist of more than just coders and hackers. New technology brings new risks and creative problem solving with a willingness to learn are the most important skills to have in this field. There are multiple career options that are not just technical. Business, medical, law, defense, and intelligence all need workers skilled in cybersecurity. For more information, check out Cyber Seeks Career Pathway map.
Roadmap To Protecting Your Devices In The Modern Cyberspace
Some tips to help shore up your device security include:
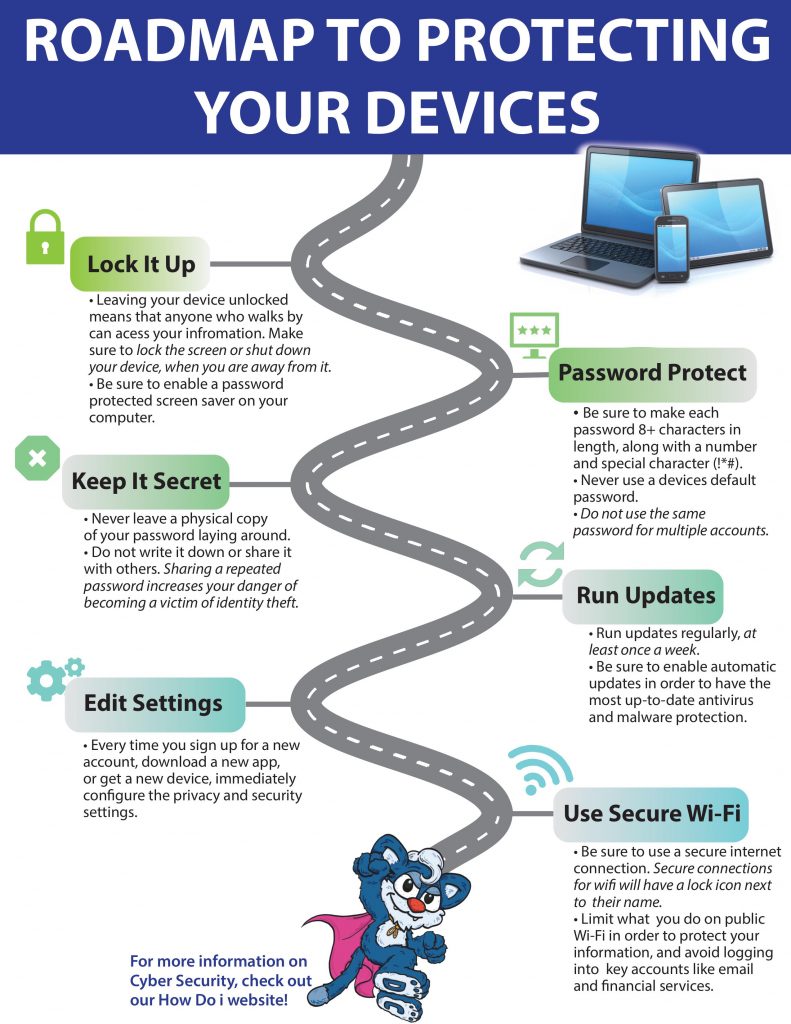
- Lock It Up: Always lock your devices and enable password protected screen savers.
- Password Protect: Use complex, different passwords for each account and device you own.
- Keep It Secret: Never write down or share your passwords or account information.
- Run Updates: Run updates regularly to protect your devices against the latest threats.
- Edit Settings: Every time you sign up for a new account or download a new app, immediately configure the privacy and security settings.
- Use Secure Wi-Fi: Limit what you do on public wi-fi and avoid logging into key accounts like financial services.
